Virtual RAM
In a virtualized computing environment, physical memory is partitioned into virtualized physical memory. Virtual memory management techniques are used to allocate additional memory to a virtual machine. Virtual RAM (vRAM) is the amount of RAM that a hypervisor allocates to a virtual server. A hypervisor has to allocate 2 GBs of vRAM to a virtual server that is being created with 2 GBs of RAM.
Note that not all allocated vRAM is physical RAM. The hypervisor may allocate both physical memory and disk space to meet the vRAM requirements, such as 1.5 GBs of physical memory and 500 MBs of RAM. This disk memory is called virtual memory, whether in the context of physical or virtual memory.
Figure 1 shows the physical memory of a compute resource being partitioned into two instances of virtualized physical memory.
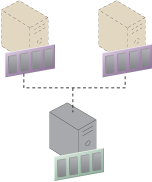
Figure 1 – An example of vRAM on two virtual servers.